FAQ
Will my data leave my device ?
- All data are stored locally, we don't upload any user data to our servers.
- Synchronization uses Apple iCloud, the data goes directly to the iCloud server.
How to set up working directory detection?
When you cut from the terminal interface to file management, the file manager will automatically open the current directory of the terminal. This function needs to be configured by ourselves. The following are the configuration steps.
- Bash
vim ~/.bash_profile
export PS1="$PS1\[\e]7;CurrentDir="'$(pwd)\a\]'
- Zsh
vim ~/.zshrc
precmd () { echo -n "\x1b]7;CurrentDir=$(pwd)\x07" }
How to connect macOS's local terminal
Due to sandbox restrictions on apps listed on the App Store, Nex Terminal cannot read local disk files, which is also for user system security reasons. However, Mac comes with an SSH service locally, and by enabling the SSH service, Nex Terminal can connect to the local terminal. The following are the configuration steps:
- Locate the '+' button in the top-left
- Select New Session,then click the button
at the top of sheet
- Create a local connection to 127.0.0.1 in Nex Terminal using the MAC system account and password
- Allowing remote login to Mac will reduce its security. If necessary, please use SSH key authentication to connect to the local terminal, or edit the configuration file /etc/ssh/sshd_comfig to add the AllowUsers user@127.0.0.1 and reject any other user's connection
Can't switch to file management on another machine after selecting file management for Alibaba Cloud bastion host?
-
Select the bastion host item, click edit, open and enable the Bastion Host SFTP settings
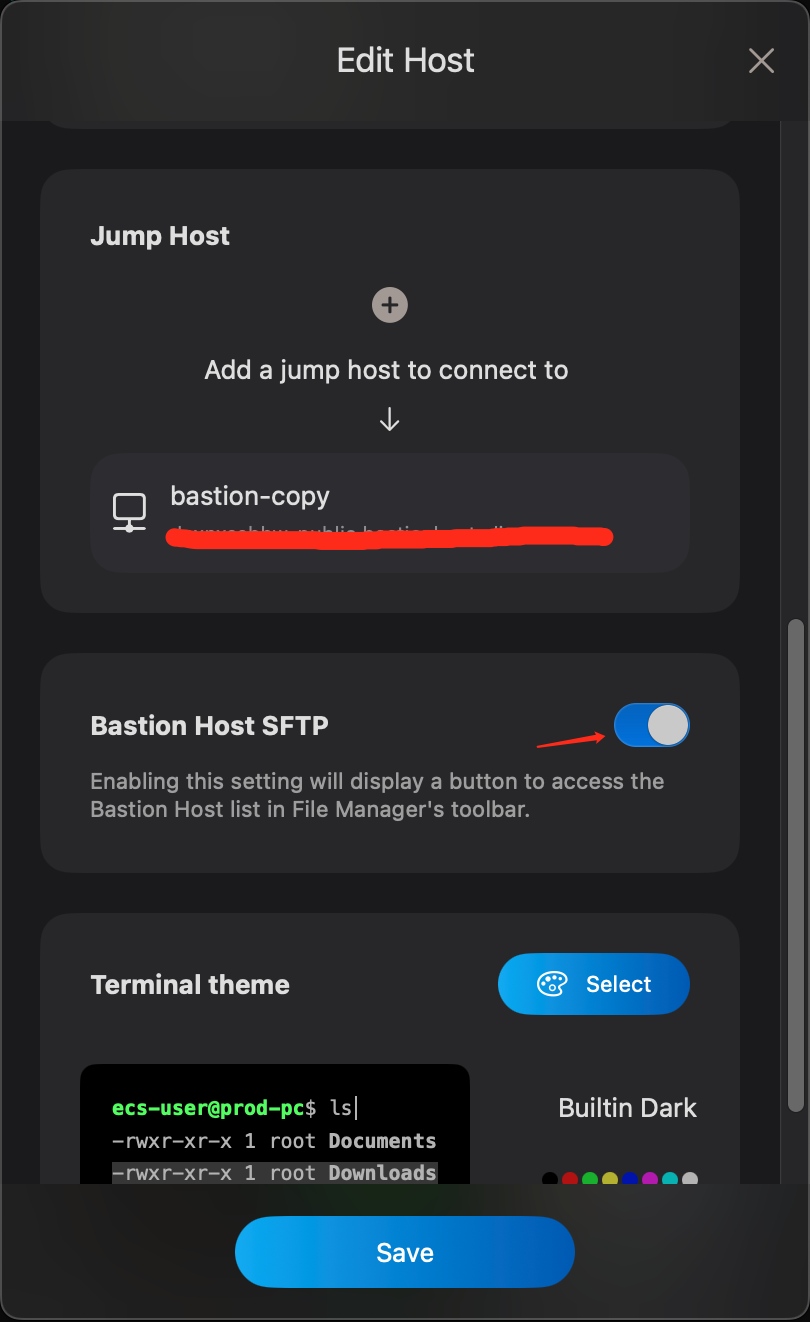
-
The File Manager interface will display a button, click this button to access the bastion host list directory
How to configure NAT?
As a developer, if you want your friend to test an HTTP API running on your localhost machine, you can utilize Nex Terminal to facilitate this process. Here's a revised step-by-step guide to help you set up the necessary configurations:
Lucy is developing a personal website on her laptop and wants William to check it out. Unfortunately, it is not reachable to William. Luckily, William can reach Lucy's public SSH server, which means that Lucy can make it possible for William to connect to her website – by configuring a remote port forwarding connection.
Here's how you can ensure everything is ready and set up the remote port forwarding rule:
-
Ensure that port 10089 is open on the SSH server host (10.23.21.11)
-
Configure GatewayPorts in /etc/ssh/sshd_config: On the SSH server host (10.23.21.11), ensure that the GatewayPorts option is set to yes in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. This allows remote port forwarding to addresses other than localhost. You can edit the file with a text editor like nano, vim, or sed:
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_configThen, find the GatewayPorts line and change it to:
GatewayPorts yesSave and close the file, then restart the SSH service to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart sshd -
Now, we can create a remote port forarding rule like this
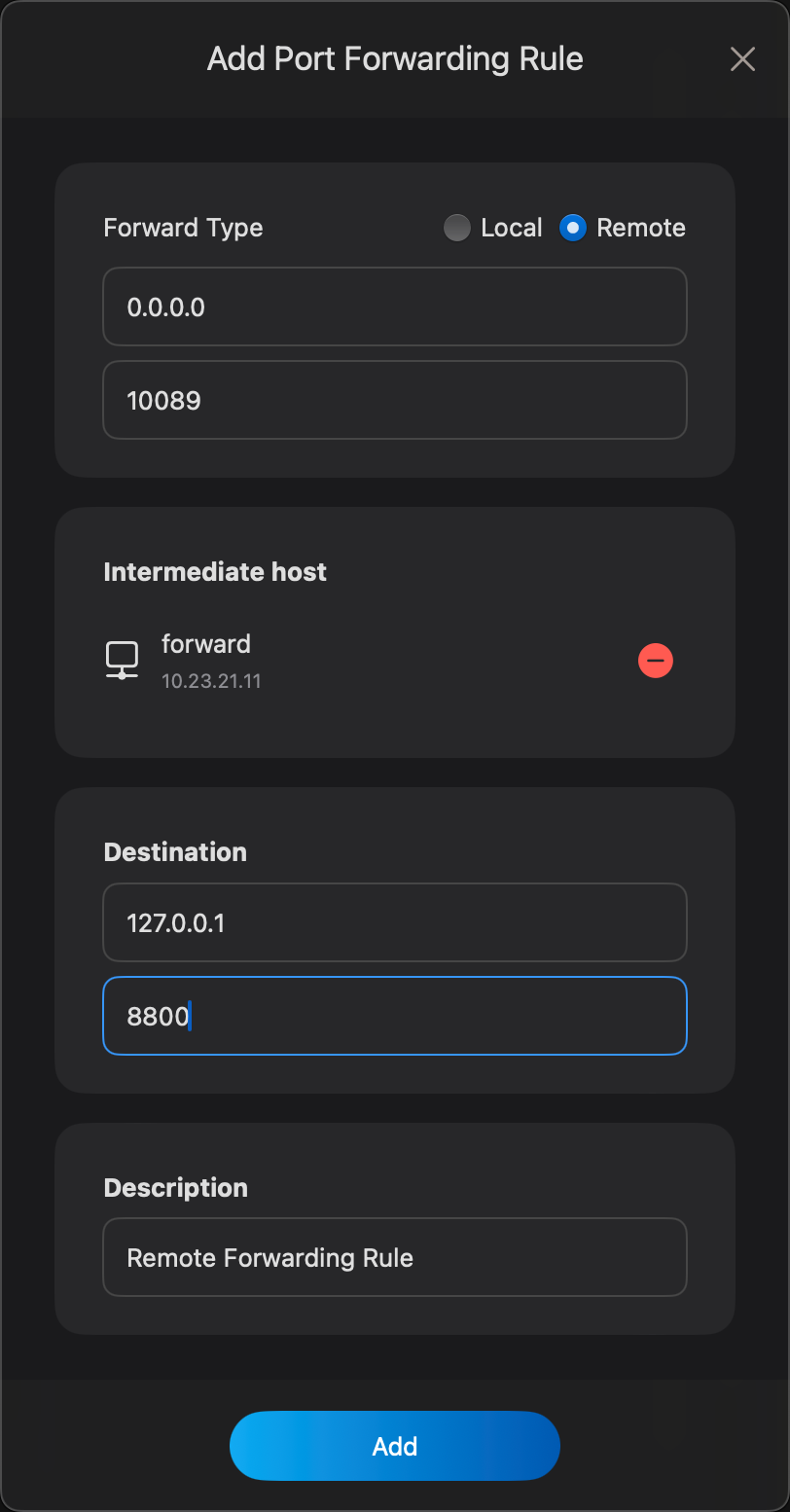
Starting this port forwarding rule,now William can access Lucy's website by using the url http://10.23.21.11:10089
- Troubleshooting
If the port forwarding is not work,you should check the port being forwarded is not used by another process, use below command to see your local listening ports
netstat -tunlp | grep 10089
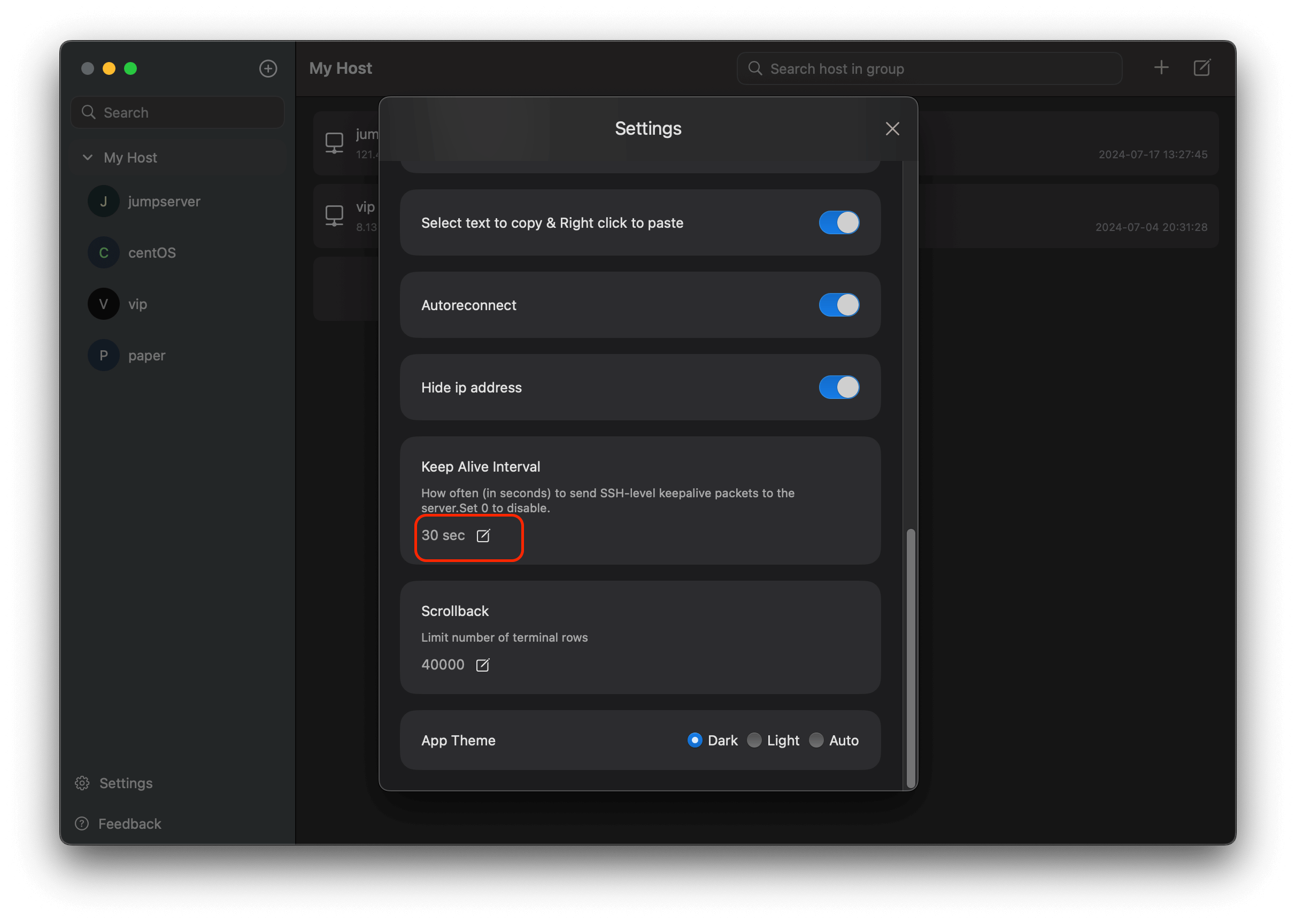
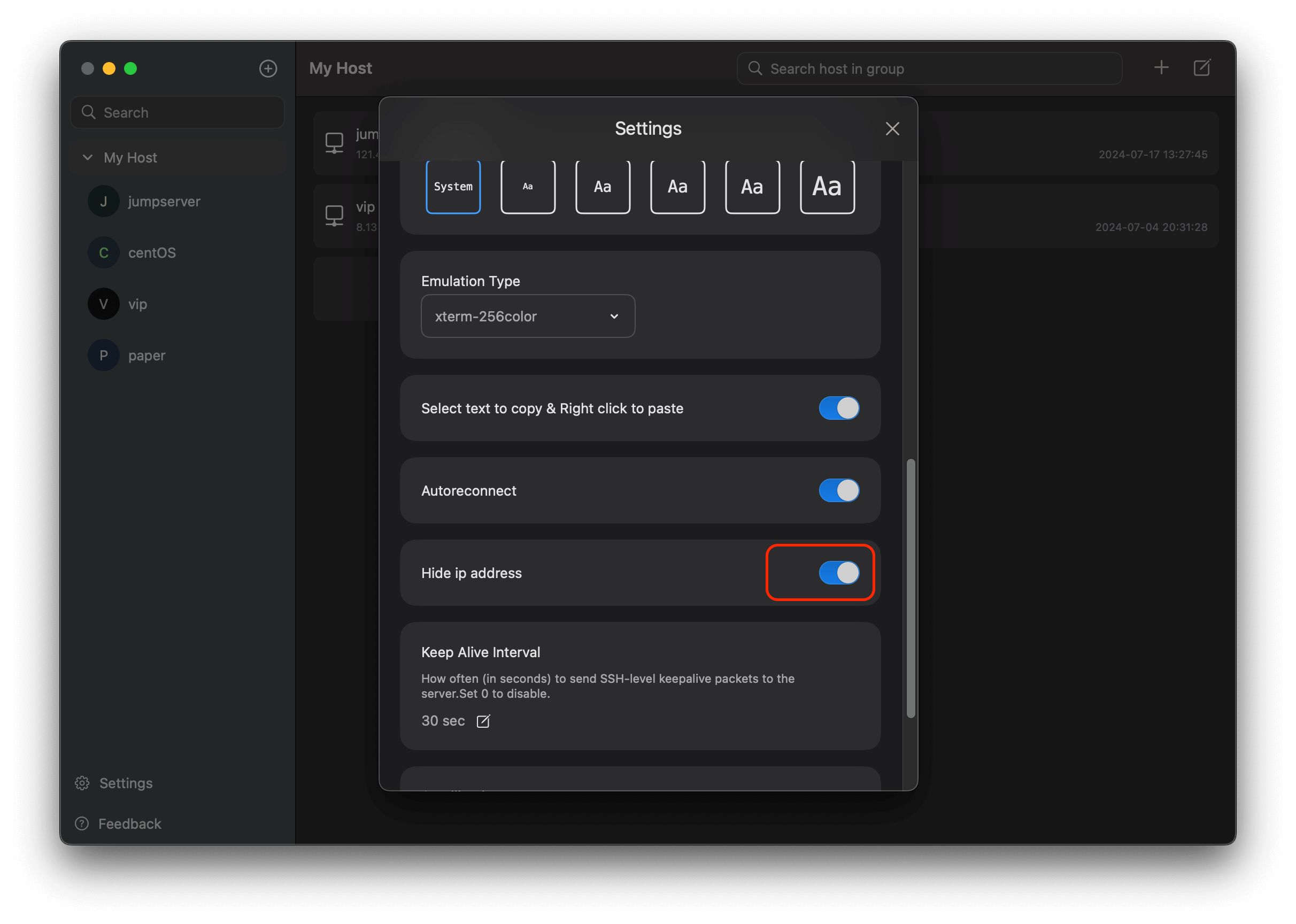
How to hide ip address in the sidebar?
in Settings dialog,just toggle the button
How to make host connection alive all the time?
Linux SSH close connection after sometime. ssh idle timeout.
What is an idle SSH session?
Here we mean that a ssh connection was made between a host and a client but there has been no activity on this connection by the user and is considered idle. Here although the ssh session is not in stuck state. You can list all the active ssh connections and then check the idle time for individual source host.
The trick to disconnect idle SSH session is to use below two arguments with proper values to achieve both the scenario i.e. to disconnect an idle SSH session and also to make sure your SSH session does not gets disconnected when idle
- ClientAliveInterval
- ClientAliveCountMax
From the man page
ClientAliveCountMax
Sets the number of client alive messages which may be sent without sshd(8) receiving any messages back from the client. If this threshold is reached
while client alive messages are being sent, sshd will disconnect the client, terminating the session. It is important to note that the use of client
alive messages is very different from TCPKeepAlive. The client alive messages are sent through the encrypted channel and therefore will not be
spoofable. The TCP keepalive option enabled by TCPKeepAlive is spoofable. The client alive mechanism is valuable when the client or server depend
on knowing when a connection has become inactive.
The default value is 3. If ClientAliveInterval is set to 15, and ClientAliveCountMax is left at the default, unresponsive SSH clients will be disconnected after approximately 45 seconds.
ClientAliveInterval
Sets a timeout interval in seconds after which if no data has been received from the client, sshd(8) will send a message through the encrypted channel to request a response from the client. The default is 0, indicating that these messages will not be sent to the client.
Disconnect idle SSH session (ssh close connection after sometime)
To disconnect idle SSH session i.e. to ssh close connection after some time make sure ClientAliveCountMax is 0. Because when is 0, sshd will not send client alive messages and ssh close connection after sometime if client is inactive for time period as provided with ClientAliveInterval.
Keep idle SSH session active
We already know how to disonnect SSH sesion,Now if this is becoming a problem for you then you can increase the value of ClientAliveCountMax to a non-zero value. Additionally you can also use TCPKeepAlive in your sshd_config on the client node. From the man page of sshd_config:
TCPKeepAlive
Specifies whether the system should send TCP keepalive messages to the other side. If they are sent, death of the connection or crash of one of the
machines will be properly noticed. However, this means that connections will die if the route is down temporarily, and some people find it annoying.
On the other hand, if TCP keepalives are not sent, sessions may hang indefinitely on the server, leaving "ghost" users and consuming server
resources.
The default is yes (to send TCP keepalive messages), and the server will notice if the network goes down or the client host crashes. This avoids in‐
finitely hanging sessions.
To disable TCP keepalive messages, the value should be set to no.
Nex Terminal supports the TCP KeepAlive function, allowing you to conveniently set the Keep Alive Interval directly within the settings dialog.